Autonomous buoy position data from Southern Ocean GLOBEC from ARSV Laurence M. Gould LMG0106 in the Southern Ocean from July 2001
Project
Programs
| Contributors | Affiliation | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Costa, Daniel P. | University of California-Santa Cruz (UCSC) | Principal Investigator |
| Fritsen, Chris H. | Desert Research Institute (DRI) | Co-Principal Investigator |
| Copley, Nancy | Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI BCO-DMO) | BCO-DMO Data Manager |
Abstract
Related datasets:
buoy_temp_barom Air temperature and barometric pressure results from autonomous buoys, Aug. - Nov. 2001
buoy_therm Thermistor data at 10 cm intervals in air, ice, water from autonomous buoys, Aug. - Nov. 2001
buoy_radm Radiometer data from autonomous buoy 07949, Aug. - Nov. 2001
During the July-September 2001 Southern Globec cruises of the Palmer and Gould we installed four buoys. Two of the buoys (07413, 07440) were standard off-the-shelf Met-Ocean Ice buoys (see above photograph). These buoys measured barometric pressure, air temperature, and GPS position. The data were transmitted via ARGOS. A radar reflector was mounted on a wooden 4 x 4 to help find the site if there was an opportunity to return, however the reflector return was difficult to discern among all the backscatter clutter caused by deformed ice and icebergs.
The other two buoys (07949, 07950) were custom made CRREL ice mass balance buoys (photo on right). These buoys reported barometric pressure, Argos position, and air temperature. In addition they had a thermistor string that measured a vertical profile of temperature, at 10 cm spacing, from the air, through the snow and ice, and into the upper ocean. There were acoustic sensors measuring the positions of the snow surface and ice bottom. A fluorometer was mounted under the ice. One of the buoys (07949) had three spectroradiometers; one mounted about the ice, one mounted directly below the ice, and one a few meters deep in the upper ocean. Results from all buoys are compared.
Tracks from all 2001 buoys:
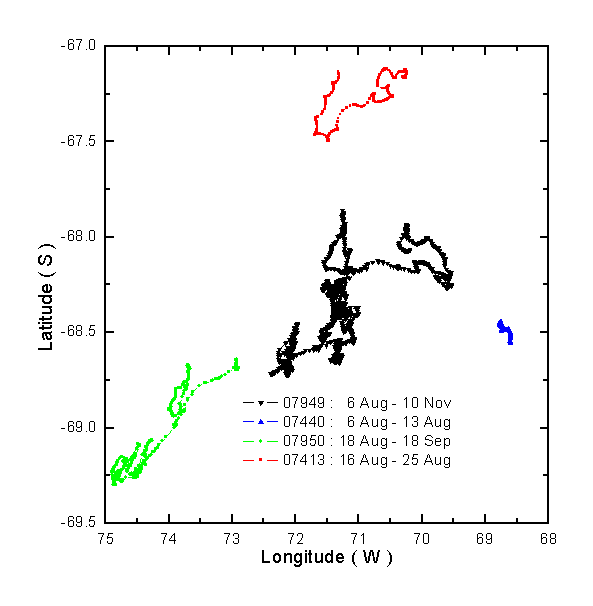
NOTE: BCO-DMO corrected lon values from positive to negative (08/15/12).
| File |
|---|
buoy_position.csv (Comma Separated Values (.csv), 170.72 KB) MD5:73ae3ab7ca828ed891f8d37a5b552e12 Primary data file for dataset ID 3114 |
| Parameter | Description | Units |
| buoy_id | identification number of the buoy | |
| inst | GPS or ARGOS type transmission | |
| yrday_gmt | GMT day and decimal time, as 326.5 for the 326th day of the year, or November 22 at 1200 hours (noon). | |
| date_gmt | gmt month, day and year, usually as a text string, e.g. feb10_1995. | |
| year | year, reported as YYYY, e.g. 1995 | |
| month_gmt | month of year, GMT time , i.e. 01-12 | |
| day_gmt | day, GMT time e.g. 22. | |
| time_gmt | time of day, reported in GMT time, 24 hour clock | |
| lat | latitude, in decimal degrees, North is positive, negative denotes South | decimal degrees |
| lon | longitude, in decimal degrees, East is positive, negative denotes West | decimal degrees |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Drifter Buoy |
| Generic Instrument Name | Drifter Buoy |
| Dataset-specific Description | Two of the buoys (07413, 07440) were standard off-the-shelf Met-Ocean Ice buoys.These buoys measured barometric pressure, air temperature, and GPS position. The data were transmitted via ARGOS. The other two buoys (07949, 07950) were custom made CRREL ice mass balance buoys (photo on right). These buoys reported barometric pressure, Argos position, and air temperature. In addition they had a thermistor string that measured a vertical profile of temperature. There were acoustic sensors measuring the positions of the snow surface and ice bottom. A fluorometer was mounted under the ice. One of the buoys (07949) had three spectroradiometers; one mounted about the ice, one mounted directly below the ice, and one a few meters deep in the upper ocean. |
| Generic Instrument Description | Drifting buoys are free drifting platforms with a float or buoy that keep the drifter at the surface and underwater sails or socks that catch the current. These instruments sit at the surface of the ocean and are transported via near-surface ocean currents. They are not fixed to the ocean bottom, therefore they "drift" with the currents. For this reason, these instruments are referred to as drifters, or drifting buoys.
The surface float contains sensors that measure different parameters, such as sea surface temperature, barometric pressure, salinity, wave height, etc. Data collected from these sensors are transmitted to satellites passing overhead, which are then relayed to land-based data centers.
definition sources: https://mmisw.org/ont/ioos/platform/drifting_buoy and https://www.aoml.noaa.gov/phod/gdp/faq.php#drifter1 |
LMG0106
| Website | |
| Platform | ARSV Laurence M. Gould |
| Report | |
| Start Date | 2001-07-21 |
| End Date | 2001-09-01 |
U.S. GLOBEC Southern Ocean (SOGLOBEC)
The fundamental objectives of United States Global Ocean Ecosystems Dynamics (U.S. GLOBEC) Program are dependent upon the cooperation of scientists from several disciplines. Physicists, biologists, and chemists must make use of data collected during U.S. GLOBEC field programs to further our understanding of the interplay of physics, biology, and chemistry. Our objectives require quantitative analysis of interdisciplinary data sets and, therefore, data must be exchanged between researchers. To extract the full scientific value, data must be made available to the scientific community on a timely basis.
GLOBEC: Sea Ice Microbial Communities (Sea Ice Microbes)
The U.S. Global Ocean Ecosystems Dynamics (U.S. GLOBEC) program has the goal of understanding and ultimately predicting how populations of marine animal species respond to natural and anthropogenic changes in climate. Research in the Southern Ocean (SO) indicates strong coupling between climatic processes and ecosystem dynamics via the annual formation and destruction of sea ice. The Southern Ocean GLOBEC Program (SO GLOBEC) will investigate the dynamic relationship between physical processes and ecosystem responses through identification of critical parameters that affect the distribution, abundance and population dynamics of target species. The overall goals of the SO GLOBEC program are to elucidate shelf circulation processes and their effect on sea ice formation and krill distribution, and to examine the factors which govern krill survivorship and availability to higher trophic levels, including penguins, seals and whales. The focus of the U.S. contribution to the international SO GLOBEC program will be on winter processes. This component will focus on the distribution and activities of sea ice microbial communities. This will be accomplished using an integrated combination of sampling (vertical profiles, horizontal surveys, and under-ice surveys) and observational protocols. Experiments will be designed to estimate microbial activity within the sea ice and at the ice-seawater interface. The research will be coordinated with components studying the water column productivity and the sea ice habitat. The result of the integrated SO GLOBEC program will be to improve the predictability of living marine resources, especially with respect to local and global climatic shifts.
U.S. GLOBal ocean ECosystems dynamics (U.S. GLOBEC)
U.S. GLOBEC (GLOBal ocean ECosystems dynamics) is a research program organized by oceanographers and fisheries scientists to address the question of how global climate change may affect the abundance and production of animals in the sea.
The U.S. GLOBEC Program currently had major research efforts underway in the Georges Bank / Northwest Atlantic Region, and the Northeast Pacific (with components in the California Current and in the Coastal Gulf of Alaska). U.S. GLOBEC was a major contributor to International GLOBEC efforts in the Southern Ocean and Western Antarctic Peninsula (WAP).
U.S. GLOBal ocean ECosystems dynamics (U.S. GLOBEC)
U.S. GLOBEC (GLOBal ocean ECosystems dynamics) is a research program organized by oceanographers and fisheries scientists to address the question of how global climate change may affect the abundance and production of animals in the sea.
The U.S. GLOBEC Program currently had major research efforts underway in the Georges Bank / Northwest Atlantic Region, and the Northeast Pacific (with components in the California Current and in the Coastal Gulf of Alaska). U.S. GLOBEC was a major contributor to International GLOBEC efforts in the Southern Ocean and Western Antarctic Peninsula (WAP).
| Funding Source | Award |
|---|---|
| NSF Antarctic Sciences (NSF ANT) |
[ table of contents | back to top ]