Seriatopora bleaching expt: temperature, salinity, light in tanks, Taiwan 2010 (MCR LTER project, Climate_Coral_Larvae project)
Project
Program
| Contributors | Affiliation | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Edmunds, Peter J. | California State University Northridge (CSUN) | Principal Investigator |
| Fan, Tung-Yung | National Museum of Marine Biology and Aquarium (NMMBA) | Scientist |
| Wall, Christopher B. | Santa Monica College (SMC) | Student |
| Copley, Nancy | Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI BCO-DMO) | BCO-DMO Data Manager |
We hypothesized that ocean acidification would cause bleaching as defined by decreased photochemical efficiency, reduced photosynthetic capacity and efficiency, depressed chlorophyll a content, and lowered Symbiodinium densities and that these effects would be exacerbated with high temperature.
Related Datasets:
Symbiodinium_Seriatopora photosynthesis
Symbiodinium_Seriatopora PI curve
Symbiodinium_Seriatopora water chemistry
These data were published in C. B. Wall, T.-Y. Fan, P. J. Edmunds (2014) Ocean acidification has no effect on thermal bleaching in the coral. Coral Reefs 33:119-13. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00338-013-1085-2.
Experimental design
Four treatments contrasted high and low temperature and pCO2:
Ambient temperature = 27.5 oC
Ambient pCO2 = 39.0 Pa
High temperature = 30.5 oC
High pCO2 = 86 Pa
Juvenile Seriatopora caliendrum were collected from Hobihu Reef, Nanwan Bay, Taiwan, and kept at the National Museum of Marine Biology and Aquarium (NMMBA), where they were placed randomly into the treatment tanks for incubations lasting 14 days. Corals were exposed to treatments in 8 tanks filled with filtered seawater. Treatments were maintained at a salinity of 33 and were monitored daily for temperature, salinity, irradiance, pH and carbonate chemistry.
Photochemical efficiency: The effects of temperature and pCO2 on photochemical efficiency were tested by measuring the maximum photochemical efficiency of open RCIIs (Type II reaction centers) in the dark (Fv/Fm) and the effective photochemical efficiency of RCII in the light (deltaF/Fm') using pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) fluorometry.
Photosynthesis-irradiance (P/I) curves: To test for the effects of pCO2 and temperature on the ability for Symbiodinium to utilize light and perform photosynthesis, net photosynthesis (P^net), determined from changes in O2 concentrations in seawater, was measured under different irradiances using three corals selected randomly from each treatment tank.
Chlorophyll-a concentration and Symbiodinium density: Chlorophyll-a concentration and Symbiodinium density were determined.
Relevant References:
For full details see Methodology, from C. B. Wall, T.-Y. Fan, P. J. Edmunds (2014) Ocean acidification has no effect on thermal bleaching in the coral. Coral Reefs 33:119-13
| File |
|---|
Symbiodinium_water_phys.csv (Comma Separated Values (.csv), 13.73 KB) MD5:cf1e9017abce91da137ffc2f7d231433 Primary data file for dataset ID 522697 |
| Parameter | Description | Units |
| lab | site of experiments | unitless |
| lat | latitude; north is positive | decimal degrees |
| lon | longitude; east is positive | decimal degrees |
| date_local | measurement date; local time | yyyy/mm/dd |
| time_local | local time of measurement | HH:MM:SS |
| tank | tanks are replicate treatments (n=2 per treatment) | unitless |
| pCO2_trt | partial pressure of carbon dioxide for each treatment; CO2 treatments are ambient vs. elevated (45 vs 85 Pa pCO2) | Pascals |
| temp_trt | temperature treatments are ambient vs. elevated (27.7 vs 30.5 C) | degrees Celsius |
| temp | measured temperature | degrees Celsius |
| sal | salinity of tank | unitless |
| PAR | Photosynthetically Available [Active] Radiation | umol photons m-2 s-1 |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Aquarium chiller |
| Generic Instrument Name | Aquarium chiller |
| Dataset-specific Description | Aquatek, Aquasystems, Taiwan |
| Generic Instrument Description | Immersible or in-line liquid cooling device, usually with temperature control. |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Conductivity Meter |
| Generic Instrument Name | Conductivity Meter |
| Dataset-specific Description | YSI 3100 Conductivity Meter, YSI Inc., USA |
| Generic Instrument Description | Conductivity Meter - An electrical conductivity meter (EC meter) measures the electrical conductivity in a solution. Commonly used in hydroponics, aquaculture and freshwater systems to monitor the amount of nutrients, salts or impurities in the water. |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Fluorometer |
| Generic Instrument Name | Fluorometer |
| Dataset-specific Description | Diving-PAM (Waltz, GmbH, Effeltrich, Germany) |
| Generic Instrument Description | A fluorometer or fluorimeter is a device used to measure parameters of fluorescence: its intensity and wavelength distribution of emission spectrum after excitation by a certain spectrum of light. The instrument is designed to measure the amount of stimulated electromagnetic radiation produced by pulses of electromagnetic radiation emitted into a water sample or in situ. |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Gas Analyzer |
| Generic Instrument Name | Gas Analyzer |
| Dataset-specific Description | Infrared (IR) gas analyzer (S151, Qubit Systems), calibrated against certified reference gas (1,793 ppm CO2, San Ying Gas Co., Taiwan). |
| Generic Instrument Description | Gas Analyzers - Instruments for determining the qualitative and quantitative composition of gas mixtures. |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Homogenizer |
| Generic Instrument Name | Homogenizer |
| Dataset-specific Description | Polytron PT2100, Kinematica, USA |
| Generic Instrument Description | A homogenizer is a piece of laboratory equipment used for the homogenization of various types of material, such as tissue, plant, food, soil, and many others. |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Immersion heater |
| Generic Instrument Name | Immersion heater |
| Dataset-specific Description | 300 watts, Taikong Corp. |
| Generic Instrument Description | Submersible heating element for water tanks and aquaria. |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | LI-COR LI-193 PAR |
| Generic Instrument Name | LI-COR LI-193 PAR Sensor |
| Generic Instrument Description | The LI-193 Underwater Spherical Quantum Sensor uses a Silicon Photodiode and glass filters encased in a waterproof housing to measure PAR (in the 400 to 700 nm waveband) in aquatic environments. Typical output is in micromol s-1 m-2. The LI-193 Sensor gives an added dimension to underwater PAR measurements as it measures photon flux from all directions. This measurement is referred to as Photosynthetic Photon Flux Fluence Rate (PPFFR) or Quantum Scalar Irradiance. This is important, for example, when studying phytoplankton, which utilize radiation from all directions for photosynthesis. LI-COR began producing Spherical Quantum Sensors in 1979; serial numbers for the LI-193 begin with SPQA-XXXXX (licor.com). |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | MFC |
| Generic Instrument Name | Mass Flow Controller |
| Dataset-specific Description | A350 Gas Concentration Controller (Qubit); solenoid-controlled |
| Generic Instrument Description | Mass Flow Controller (MFC) - A device used to measure and control the flow of fluids and gases |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | pump |
| Generic Instrument Name | Pump |
| Dataset-specific Description | To mix water in tanks |
| Generic Instrument Description | A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they use to move the fluid: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Automatic titrator |
| Generic Instrument Name | Titrator |
| Dataset-specific Description | Open-cell autotitrator (Model DL50, Mettler-Toledo, USA) filled with certified acid titrant (from A. Dickson, Scripps Institution of Oceanography) and equipped with a DG115-SC pH probe (Mettler-Toledo). |
| Generic Instrument Description | Titrators are instruments that incrementally add quantified aliquots of a reagent to a sample until the end-point of a chemical reaction is reached. |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Water Temp Sensor |
| Generic Instrument Name | Water Temperature Sensor |
| Dataset-specific Description | 1. Microsensor-based temperature regulators (AquaController, Neptune Systems, USA)
2. Certified digital thermometer (Fisher Scientific 15-077-8, ± 0.05 C) |
| Generic Instrument Description | General term for an instrument that measures the temperature of the water with which it is in contact (thermometer). |
lab_Edmunds_NMMBA
| Website | |
| Platform | Natl Museum Mar. Bio. and Aquar. Taiwan |
| Start Date | 2010-03-18 |
| End Date | 2010-03-24 |
| Description | Experiments related to the research project: 'RUI- The ecophysiological basis of the response of coral larvae and early life history stages to global climate change' were conducted at the laboratories of the National Museum of Marine Biology and Aquarium in Southern Taiwan. |
Moorea Coral Reef Long-Term Ecological Research site (MCR LTER)
NSF Award Abstract:
Coral reefs provide important benefits to society, from food to exceptional biodiversity to shoreline protection and recreation, but they are threatened by natural perturbations and human activities, including those causing global-scale changes. These pressures increasingly are causing coral reefs to undergo large, often abrupt, ecological changes where corals are being replaced by seaweeds or other undesirable organisms. Historically, the major agent of disturbance to coral reefs has been powerful storms, but in recent decades, episodes of mass coral bleaching from marine heat waves have become more frequent and severe as the temperature of ocean surface waters continues to rise. Coral reefs are further stressed by local human activities that cause nutrient pollution and deplete herbivorous fishes that control growth of seaweeds. Studying how coral reefs respond to these two types of disturbance under different levels of nutrient pollution and fishing provides essential information on what affects the ability of coral reefs to buffer environmental change and disturbances without collapsing to a persistent, degraded condition. The fundamental goals of the Moorea Coral Reef Long Term Ecological Research program (MCR LTER) are to understand how and why coral reefs change over time, to assess the consequences of these changes, and to contribute scientific knowledge needed to sustain coral reef ecosystems and the important societal services they provide. This research improves understanding and management of coral reefs, which benefits all groups concerned with the welfare of this ecologically, economically and culturally important ecosystem. In addition to academic communities, scientific findings are communicated to interested individuals, non-governmental organizations, island communities and governmental entities. These findings also are integrated into K-12, undergraduate, graduate and public education activities through a multi-pronged program that includes inquiry-based curricula, interactive and media-based public education programs, and internet-based resources. MCR?s research, training, education and outreach efforts all emphasize broadening participation in STEM fields and strengthening STEM literacy.
New research activities build on MCR LTER?s powerful foundation of long-term observations and broad ecological understanding of oceanic coral reefs to address the following core issues: How is the changing disturbance regime (recurrent heat waves in addition to cyclonic storms) altering the resilience of coral reefs, and what are the ecological consequences of altered resilience? Research activities are organized around a unifying framework that explicitly addresses how reef communities are affected by the nature and history of coral-killing disturbances, and how those responses to disturbance are influenced by the pattern of local human stressors. New studies answer three focal questions: (1) How do different disturbance types, which either remove (storms) or retain (heat waves) dead coral skeletons, affect community dynamics, abrupt changes in ecological state, and resilience? (2) How do local stressors interact with new disturbance regimes to create spatial heterogeneity in community dynamics, ecosystem processes, and spatial resilience? And (3) What attributes of coral and coral reef communities influence their capacity to remain resilient under current and future environmental conditions? These questions provide an unparalleled opportunity to test hypotheses and advance theory regarding ecological resilience and the causes and consequences of abrupt ecological change, which is broadly relevant across aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
This award reflects NSF's statutory mission and has been deemed worthy of support through evaluation using the Foundation's intellectual merit and broader impacts review criteria.
From http://www.lternet.edu/sites/mcr/ and http://mcr.lternet.edu/:
The Moorea Coral Reef LTER site encompasses the coral reef complex that surrounds the island of Moorea, French Polynesia (17°30'S, 149°50'W). Moorea is a small, triangular volcanic island 20 km west of Tahiti in the Society Islands of French Polynesia. An offshore barrier reef forms a system of shallow (mean depth ~ 5-7 m), narrow (~0.8-1.5 km wide) lagoons around the 60 km perimeter of Moorea. All major coral reef types (e.g., fringing reef, lagoon patch reefs, back reef, barrier reef and fore reef) are present and accessible by small boat.
The MCR LTER was established in 2004 by the US National Science Foundation (NSF) and is a partnership between the University of California Santa Barbara and California State University, Northridge. MCR researchers include marine scientists from the UC Santa Barbara, CSU Northridge, UC Davis, UC Santa Cruz, UC San Diego, CSU San Marcos, Duke University and the University of Hawaii. Field operations are conducted from the UC Berkeley Richard B. Gump South Pacific Research Station on the island of Moorea, French Polynesia.
MCR LTER Data: The Moorea Coral Reef (MCR) LTER data are managed by and available directly from the MCR project data site URL shown above. The datasets listed below were collected at or near the MCR LTER sampling locations, and funded by NSF OCE as ancillary projects related to the MCR LTER core research themes.
This project is supported by continuing grants with slight name variations:
- LTER: Long-Term Dynamics of a Coral Reef Ecosystem
- LTER: MCR II - Long-Term Dynamics of a Coral Reef Ecosystem
- LTER: MCR IIB: Long-Term Dynamics of a Coral Reef Ecosystem
- LTER: MCR III: Long-Term Dynamics of a Coral Reef Ecosystem
- LTER: MCR IV: Long-Term Dynamics of a Coral Reef Ecosystem
The ecophysiological basis of the response of coral larvae and early life history stages to global climate change (Climate_Coral_Larvae)
Tropical coral reefs face a suite of environmental assaults ranging from anchor damage to the effects of global climate change (GCC). The consequences are evident throughout the tropics, where many coral reefs have lost a substantial fraction of their coral cover in a few decades. Notwithstanding the importance of reducing the impacts of environmental stresses, the only means by which these ecosystems can recover (or simply persist) is through the recruitment of scleractinians, which is a function of successful larval development, delivery, settlement, metamorphosis, and post-settlement events. Despite wide recognition of the importance of these processes, there are few pertinent empirical data, and virtually none that address the mechanisms mediating the success of early coral life stages in a physical environmental varying at multiple spatio-temporal scales.
The objective of this research is to complete one of the first comprehensive ecophysiological analyses of the early life stages of corals through a description of: (1) their functionality under 'normal' conditions, and (2) their response to the main drivers of GCC. These analyses will be completed for 2 species representative of a brooding life history strategy, and the experiments will be completed in two locations, one (Taiwan) that provides unrivalled experience in coral reproductive biology, and superb microcosm facilities, and the other (Moorea), with access to a relatively pristine environment, a well described ecological and oceanographic context (through the MCR-LTER), and the capacity to bring a strong biogeographic contrast to the project. The results of the study will be integrated through modeling to explore the effects of GCC on coral community structure over the next century.
The following publications and data resulted from this project:
2013 Wall CB, Fan TY, Edmunds PJ. Ocean acidification has no effect on thermal bleaching in the coral Seriatopora caliendrum. Coral Reefs 33: 119-130.
Symbiodinium_Seriatopora photosynthesis
Symbiodinium_Seriatopora PI curve
Symbiodinium_Seriatopora temp-salinity-light
Symbiodinium_Seriatopora water chemistry
- Download complete data for this publication (Excel file)
2013 Wall CB, Edmunds PJ. In situ effects of low pH and elevated HCO3- on juvenile Porites spp. in Moorea, French Polynesia. Biological Bulletin 225:92-101.
Data at MCR and PANGEA: doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.833913
- Download complete data for this publication (Excel file)
2013 Vivian R Cumbo, Peter J Edmunds, Christopher B Wall, Tung-Yung Fan. Brooded coral larvae differ in their response to high temperature and elevated pCO2 depending on the day of release. Marine Biology DOI 10.1007/s00227-013-2280-y.
Data also at PANGEA: doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.831612
brooded coral larvae 2 - carbonate chemistry
brooded coral larvae 2 - larval release March 2003-2008
brooded coral larvae 2 - respiration_photosyth_mortality
- Download complete data for this publication (Excel file)
2013 Edmunds PJ, Cumbo VR, Fan TY. Metabolic costs of larval settlement and metamorphosis in the coral Seriatopora caliendrum under ambient and elevated pCO2. Journal Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 443: 33-38 Data also at PANGEA: doi:10.1594/PANGAEA.821644
Coral post-settlement physiology
- Download complete data for this publication (Excel file)
2013 Aaron M Dufault, Aaron Ninokawa, Lorenzo Bramanti, Vivian R Cumbo, Tung-Yung Fan, Peter J Edmunds. The role of light in mediating the effects of ocean acidification on coral calcification. Journal of Experimental Biology 216: 1570-1577.
coral-light expt.- PAR
coral-light expt.- carbonate chemistry
coral-light expt.- temp_salinity
coral-light expt.- growth
coral-light expt.- protein
coral-light expt.- survival
- Download complete data for this publication (Excel file)
2012 Cumbo, VR, Fan TY, Edmunds PJ. Effects of exposure duration on the response of Pocillopora damicornis larvae to elevated temperature and high pCO2. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 439: 100-107.
Data is also at PANGEA: doi:10.1594/PANGAEA.823582
brooded coral larvae 3 - carbonate chemistry
brooded coral larvae 3 - light
brooded coral larvae 3 - mortality
brooded coral larvae 3 - protein
brooded coral larvae 3 - respiration and protein
brooded coral larvae 3 - respiration raw data
brooded coral larvae 3 - symbiont density
brooded coral larvae 3 - tank temperature
- Download part 1 of data for this publication (Excel file)
- Download tank parameters data for this publication (Excel file)
2012 Cumbo, VR, Fan TY, Edmunds PJ. Physiological development of brooded larvae from two pocilloporid corals in Taiwan. Marine Biology 159: 2853-2866.
brooded coral - carbonate chemistry
brooded coral - release
brooded coral - respiration
brooded coral - settlement competency
brooded coral - size_July
brooded coral - size_protein_symbionts_photosynth
- Download complete data for this publication (Excel file)
2012 Dufault, Aaron M; Vivian R Cumbo; Tung-Yung Fan; Peter J Edmunds. Effects of diurnally oscillating pCO2 on the calcification and survival of coral recruits. Royal Society of London (B) 279: 2951-2958. doi:10.1098/rspb.2011.2545
Data is also at PANGEA: doi:10.1594/PANGAEA.830185
recruit_growth_area
recruit_growth_weight
recruit_seawater_chemistry
recruit_survival
- Download complete data for this publication (Excel file)
2011 Edmunds PJ, Cumbo V, Fan TY. Effects of temperature on the respiration of brooded larvae from tropical reef corals. Journal of Experimental Biology 214: 2783-2790.
CoralLarvae_comparison_respir
CoralLarvae_release
CoralLarvae_respir
CoralLarvae_size
- Download complete data for this publication (Excel file)
Long Term Ecological Research network (LTER)
adapted from http://www.lternet.edu/
The National Science Foundation established the LTER program in 1980 to support research on long-term ecological phenomena in the United States. The Long Term Ecological Research (LTER) Network is a collaborative effort involving more than 1800 scientists and students investigating ecological processes over long temporal and broad spatial scales. The LTER Network promotes synthesis and comparative research across sites and ecosystems and among other related national and international research programs. The LTER research sites represent diverse ecosystems with emphasis on different research themes, and cross-site communication, network publications, and research-planning activities are coordinated through the LTER Network Office.
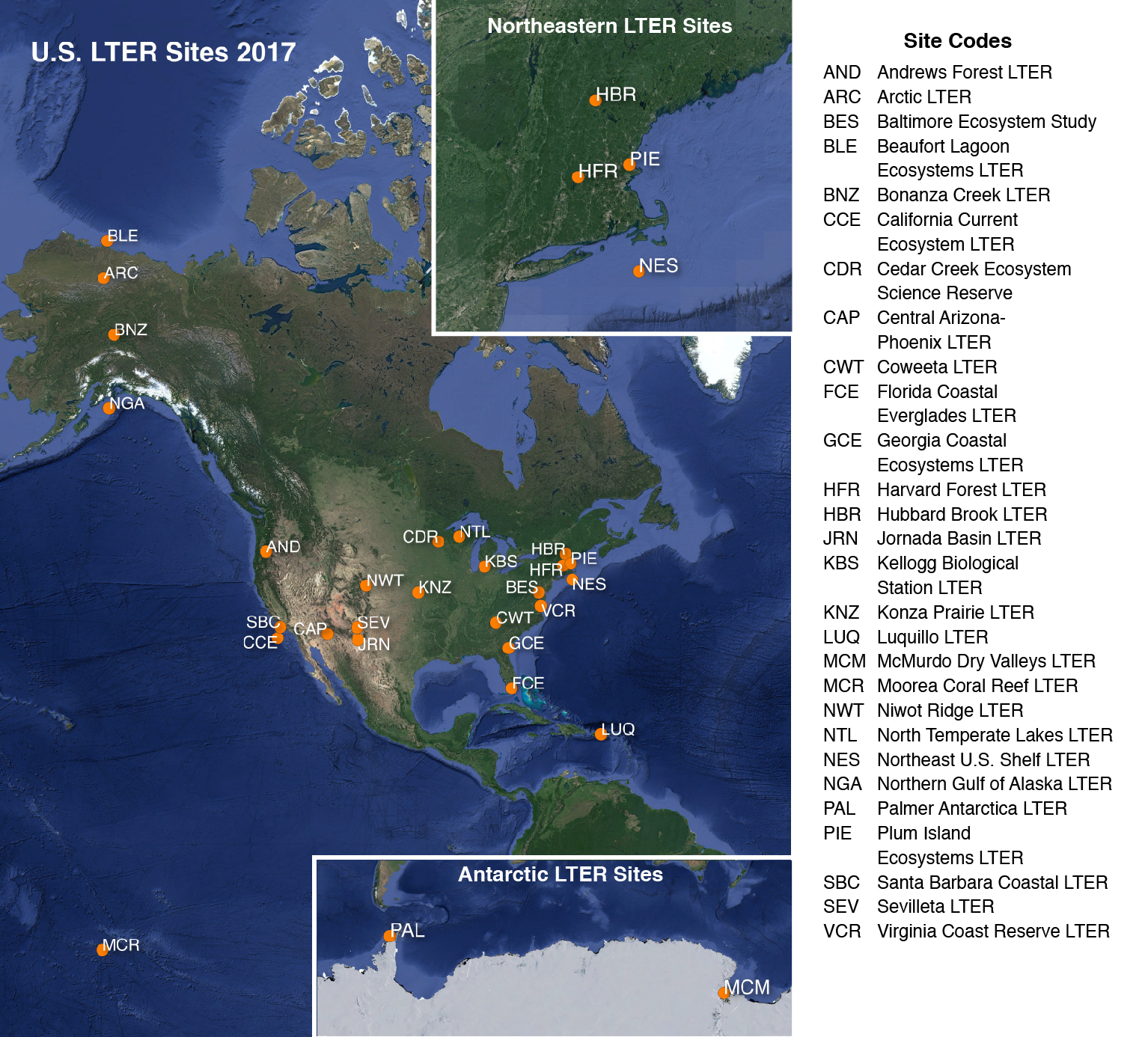
2017 LTER research site map obtained from https://lternet.edu/site/lter-network/
| Funding Source | Award |
|---|---|
| NSF Division of Ocean Sciences (NSF OCE) |
[ table of contents | back to top ]